
SURGICAL REMOVAL OF DENTAL CYSTS
What is a dental cyst?
A dental cyst is a fluid-filled sac of tissue in your gums and/or jawbone. Most of the time, a cyst is painless. There are many different types of dental cysts.
What are the different types of dental cysts?
The different types of dental cysts are:
- Dentigerous cysts,
- Periapical cysts, and
- Odontogenic keratocysts.
Where can dental cysts be found?
Dental cysts can be found around the roots of dead/infected teeth, within the gums, around impacted wisdom teeth, in your maxillary sinuses or within the jawbone.
What problems can dental cysts cause?
Dental cysts may cause these problems:
- Pain and/or swelling due to infection
- Weakening of the jawbone from expansion of the cyst
- Migration of teeth that are being pushed aside by the growing cyst
- Breathing and sleep problems related to sinus issues.
Symptomless dental cysts can remain undetected for months or years.
What are the common symptoms of dental cysts?
There is usually no obvious dental cyst symptom. In fact, most of the patients we see do not realise that they have a dental cyst until it gets infected. However, we have realised that patients with dental cysts often come to the clinic with the following conditions or problems:
- Teeth sensitivity
- Displacement of teeth
- Loose teeth
- Gum swelling
- Gum discomfort
- Facial numbness from cyst pressing onto a nerve
How do I know if I have a dental cyst?
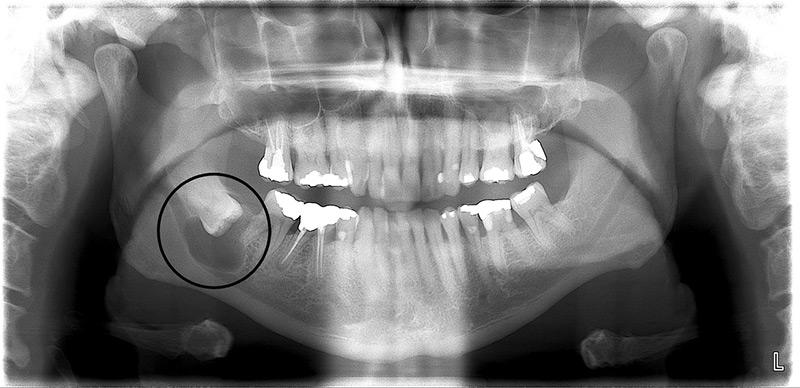
A small dental cyst developing inside the jawbone may be visible on an X-ray. Larger cysts may cause a firm facial swelling to appear. Your teeth may also start migrating rapidly in the area affected by the cyst.
Confirmation of the cyst diagnosis is done from a tissue sample (biopsy) taken during surgical removal of the lesion. There are other tumours that may resemble cysts, but are treated very differently.
Periodic dental x-rays are essential for identification of dental cysts and other bony abnormalities.
How are dental cysts treated?
There are two ways to treat a dental cyst:
- Surgery – for the removal of all types of cysts or tumours.
- Endodontic Therapy – This is done in conjunction with surgical removal if the cyst is associated with an infected root canal.
Surgical Removal of Dental Cyst at Elite Dental
Step 1: Detection
Dental cysts are normally picked up during a routine examination,which includes dental x-rays.
Your dentist may order a 3D CBCT scan that will provide more information about the cyst and its relationship with surrounding teeth and other structures (nerves, sinuses) within the bone.
Step 2: Pre-surgical preparation
A few days before, a thorough scaling and polishing is done. An oral probiotic is also given to boost the numbers of beneficial bacteria in the saliva so that healing is smooth.
If you require root canal treatment, this will be completed prior to the surgery.
Step 3: Removing the cyst
The cyst is removed by our in-house oral surgeon through a window in the bone under a local anaesthetic. You may also choose to be sedated for the entire procedure to ensure an anxiety free experience.
If there is a tooth embedded within the cyst, it might also be removed. Bone grafting material may also be placed to fill the void left behind after the cyst is removed. Stitches will be placed in the gums afterward. These will be removed after a few days.
The excised tissue can be sent to a pathology lab to be identified under microscope. This is important for identifying other types of tumours that may resemble cysts.
Can I treat a dental cyst at home?
The fast answer is yes, it is possible for you to treat your dental cyst at home. In the event where your dental cyst is small or mild with no inflammation, it is possible for you or a patient to treat dental cysts with antibiotics.
Some patients are also able to use a home remedy to treat dental cysts. However, it is still strongly advised that patients visit a trusted dentist before attempting any home remedy or self-treatment.
Is a dental cyst removal painful?
A dental cyst removal should not be painful.




